- Published on
SpaceX Starship Flight 5: A New Era in Space Exploration
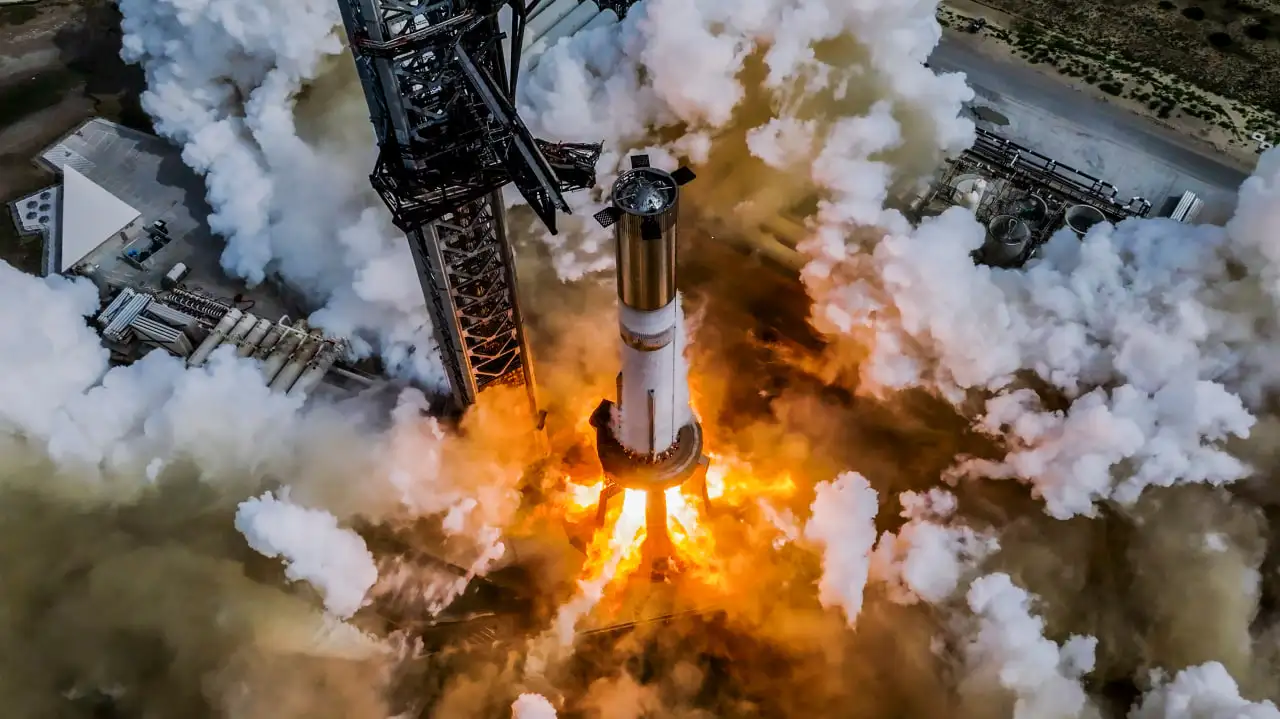
SpaceX’s Starship Flight 5 left the world in awe with two extraordinary feats: the Super Heavy booster landed gently using a giant pair of chopstick-like arms, and the Starship splashdown completed the mission, laying the groundwork for a new era of space exploration. This was not just another test flight—it was an engineering masterpiece.
%3Ano_upscale()%3Aformat(webp)%2Fcdn.vox-cdn.com%2Fuploads%2Fchorus_asset%2Ffile%2F25674955%2FSuper_Heavy_Booster_catch.gif&w=3840&q=75)
Engineering Brilliance: From Concept to Reality
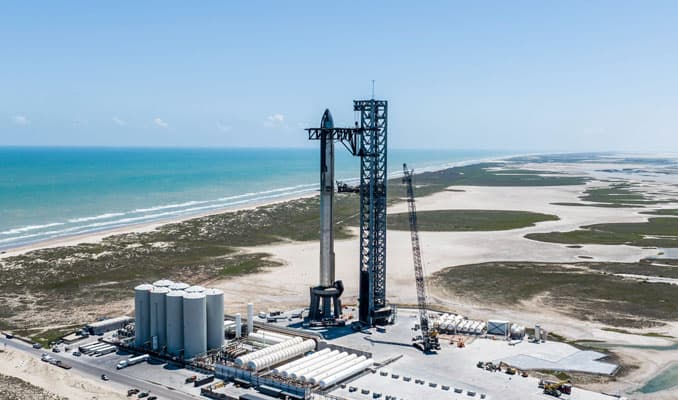
Starship Flight 5 is more than just a technical success. It represents the culmination of decades of research, development, and innovation. SpaceX had to solve countless engineering challenges to make this happen—from designing and building the Raptor engines that power the massive Starship system to perfecting the software that controls the precision landing of a 69-meter booster.
The 33 Raptor engines powering the booster, each generating over 230 metric tons of thrust, must work in perfect synchrony, and each one needs to be reliable enough for rapid reuse—a cornerstone of SpaceX’s vision for reducing costs in space travel.

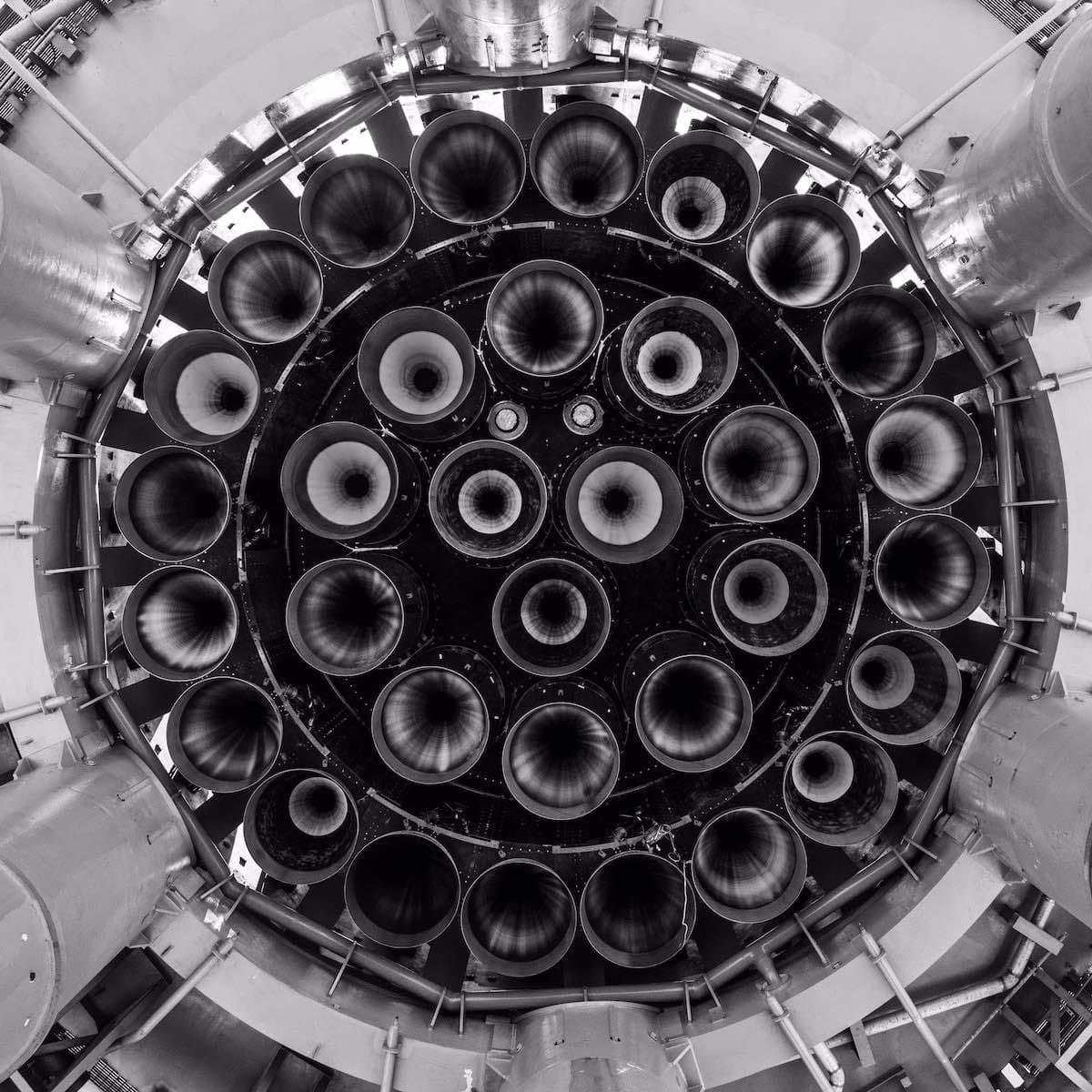



A Technological and Logistical Triumph
One of the most complex aspects of Starship Flight 5 was landing the Super Heavy Booster using the giant "chopstick" arms on the launch tower. Traditional rocket landings use landing legs and wide landing pads, but SpaceX’s approach significantly reduces turnaround time by catching the booster directly at the launch site, ready for refurbishment and reuse.
This level of precision landing and recovery has the potential to revolutionize not only space travel but also the broader aerospace industry. By cutting turnaround times and eliminating complex ground logistics, SpaceX is bringing us closer to a future where launching rockets could become as routine as boarding an airplane.

Major Milestones in SpaceX History
Let’s take a step back and look at the key events that shaped SpaceX into what it is today:
Falcon 1: The First Private Rocket to Orbit (2008)
Falcon 1: The First Private Rocket to Orbit (2008)
In 2008, SpaceX made history when Falcon 1 became the first privately developed liquid-fueled rocket to reach orbit. This success proved that private companies could not only participate in space exploration but could lead it. Falcon 1’s development was plagued with challenges—multiple failures before its historic fourth flight—but it laid the foundation for what was to come.
Falcon 9: The First Reusable Rocket (2015)
In 2015, SpaceX achieved a game-changing milestone when Falcon 9’s booster landed safely after propelling a payload to space. It marked the first time a reusable rocket had ever returned to Earth and landed intact. This breakthrough dramatically lowered the cost of space missions and opened the door to more frequent, affordable space travel.
Falcon Heavy: The Iconic Dual Landing (2018)
Falcon Heavy’s launch in 2018, with its two side boosters landing simultaneously, became one of the most iconic images in space history. This success was a clear demonstration of SpaceX’s expertise in reusable rocketry and its ability to manage complex missions.

The Economics of Space: Lowering the Costs
Space exploration has historically been prohibitively expensive, with each mission costing hundreds of millions, if not billions, of dollars. But SpaceX’s focus on reusability is fundamentally changing the economics of space travel. The Falcon 9 is already reducing launch costs by reusing boosters, and Starship aims to do the same on a larger scale.
Here’s how costs have been reduced over time:
| Rocket | Cost Per Launch | Reusable? |
|---|---|---|
| Falcon 1 | $7 million | No |
| Falcon 9 (early) | $62 million | Partially |
| Falcon 9 (reusable) | $50-60 million | Yes |
| Starship (projected) | $2 million | Yes |
Projected Starship costs of $2 million per launch will make space exploration accessible to more industries and countries, dramatically lowering the barrier for entering space.
Conclusion: The Future is Here
SpaceX's Starship Flight 5 is not just another milestone—it represents a transformative moment for humanity's future in space. By conquering the immense engineering challenges and logistical complexities involved in catching boosters with chopsticks and reusing spacecraft, SpaceX has shown the world that a multi-planetary civilization is within our reach.
The vision is clear: space travel will soon become affordable, sustainable, and routine. We are on the cusp of an era where missions to Mars, the Moon, and beyond are not the dream of a distant future, but the reality of today. Space has changed forever, and this is just the beginning.